Key Themes from the Fakuma Show
Close Up on Technology
Servo-hydraulics, servo sprue pickers, electronic water-flow monitoring/control, and exotic multi-process cells were the headliners in Friedrichshafen.
Some people call it the “mini K Show.” The Fakuma exhibition in Friedrichshafen, Germany, used to be considered a local plastics trade fair for German machinery exhibitors to reach an audience in southern Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and the Czech Republic. But the show has grown continuously in importance, and Fakuma 2014 attracted nearly 46,000 visitors from 117 countries and 1772 exhibitors from 36 nations.
It’s still predominantly an injection molding machinery show. Among the equipment introductions at Fakuma, four categories stood out because they were highlighted by multiple exhibitors.
1. SERVO PUMPS ARE THE NEW STANDARD FOR HYDRAULICS
Most machine builders are coming around to the idea that the future of hydraulics in injection molding—and it probably does have a future for a long while to come—is using pumps with variable-speed servo or frequency drives.
For example, officials from Arburg (U.S. office in Newington, Conn.) ackowledged that “there is a clear trend toward servo hydraulics for energy savings and noise reduction.” Confirming that trend, several machine builders introduced presses with servo hydraulics as standard instead of an option that used to cost around 10% additional but provided energy savings nearly equivalent to those of an all-electric machine.
• Wittmann Battenfeld (U.S. office in Torrington, Conn.;) introduced the SmartPower series that will replace the conventional hydraulic HM series in sizes from 25 to 120 metric tons at no extra cost. They reportedly cost about 20% less than an all-electrics for equivalent energy consumption.
• Sumitomo (SHI) Demag Plastics Machinery (U.S. office Strongsville, Ohio) brought out the System Servo series. They do cost a bit more than standard Systec models, but Sumitomo says 60-70% of those machines are being sold with servo pumps anyway.
• KraussMaffei (U.S. office in Florence, Ky.) has revised and upgraded its CX Series in smaller sizes (35 to 160 m.t.) with servo hydraulics now standard. A company official said, candidly, that there is no increase in list price, but discounts might be less than before.
• Haitian of China (U.S. representative is Absolute Haitian in Worcester, Mass.) has new smaller models of its servo-hydraulic, two-platen Jupiter II series, starting at 450 m.t.
• Engel (U.S. office in York, Pa.) still offers servo hydraulics as an option, but it’s one that 70% of its hydraulic machine customers purchase.
• Boy Machines (U.S. office in Exton, Pa.) already makes servo hydraulics standard on all its machines except its very smallest XS model (10 m.t.). Boy sees no further advantage in—and therefore does not offer—all-electrics.
2. SPRUE PICKERS GO SERVO
Servo-powered sprue pickers were a hot button at Fakuma, promising more speed and precision than pneumatics, plus lower energy consumption.
• Wittmann Battenfeld introduced the WS80 servo picker with a rotary axis and two linear axes. It’s designed to operate within the machine guards.
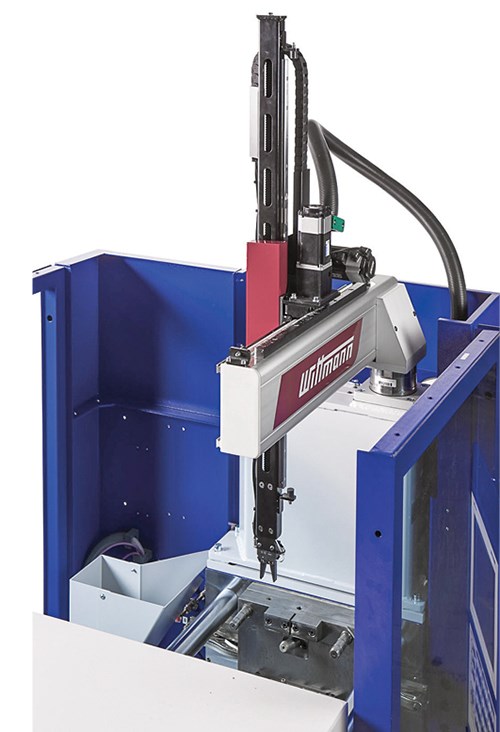
• KraussMaffei showed off its new SPX10 servo picker, also with a rotary axis and telescoping vertical arm. It operates within the machine envelope.
• Engel introduced the servo-driven e-pic, which is distinctive for its jointed vertical arm and an additional telescoping action.
• While not new, Arburg showed its two-year-old swiveling servo picker.
• Sepro (U.S. office in Pittsburgh) showed its S3 swiveling servo picker, which also appeared at Fakuma 2013 and K 2013.
• Boy operated its year-old swiveling sprue picker—a pneumatic model.
3. MOLD COOLING GETS MORE ATTENTION
Injection machine suppliers are now addressing mold cooling as a process variable that has received far less attention than other sources of quality and productivity fluctuations.
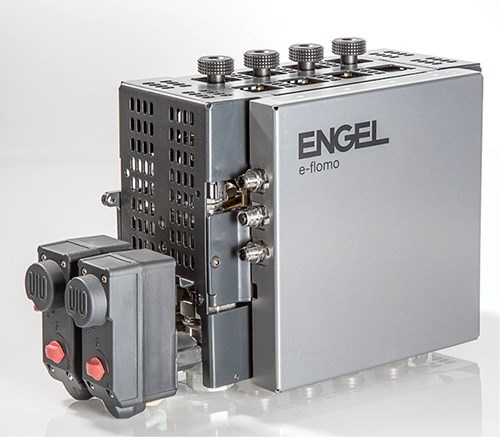
• Engel introduced the e-flomo water manifold that automatically monitors water pressure and temperature and adjusts water-flow valves to compensate for filter clogging and system pressure variations.
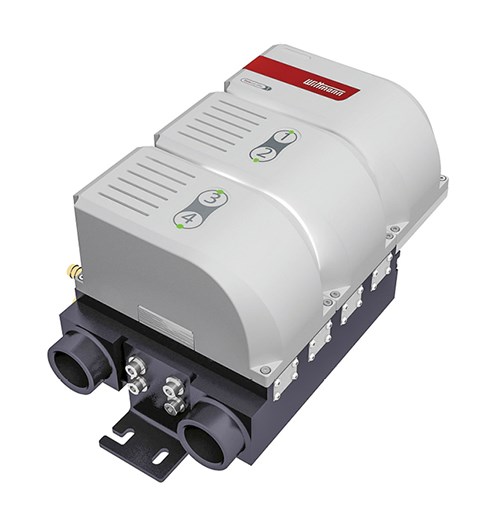
• Wittmann Battenfeld showed its new ultrasonic flow monitor for Tempro plus D series TCUs that now operates at higher temperatures (160-180 C) and measures flow rates down to 0.5 liter/min with ± 5% accuracy. Also new is the Flowcon plus water regulator, which controls either temperature or flow rate for each individual water circuit. It’s aimed particularly at water up to 100 C and measures flow in a noncontact manner from 1 to 15 l/min. Wittmann says more than half of its mold-temperature controllers are now sold with a flow-regulation device.
• KraussMaffei operated an all-electric AX machine with a flow-monitoring system integrated into the MC6 machine controller to document the mold heat balancing for quality records.
• ONI Temperiertechnik Rhytemper GmbH of Germany showed off its new-generation Rhytemper FlowWatch water-distribution/flow controller with electronic flow and temperature monitoring for each mold circuit. The flow may be adjusted by a manual or motorized control valve in the individual circuits. Automatic control via the new FlowControl system uses electronic proportional valves and pulsed water cooling without a heating or recirculation system. Pulse timing is adjusted separately for each individual circult.
Compact design allows installation close to the tool on the injection machine, reducing hose lengths and pressure losses. ONI also introduced a central touchscreen terminal for continuous control and monitoring of mold-cooling circuits on multiple machines.
4. INTEGRATED MULTI-PROCESS CELLS
Some of the most dazzling exhibits at recent plastics exhibitions have demonstrated intimate pairings of injection molding with other processes in an integrated cell. Fakuma 2014 was no exception. It showed how machinery OEMs are pulling out the stops to show that virtually anything can be integrated with injection molding.
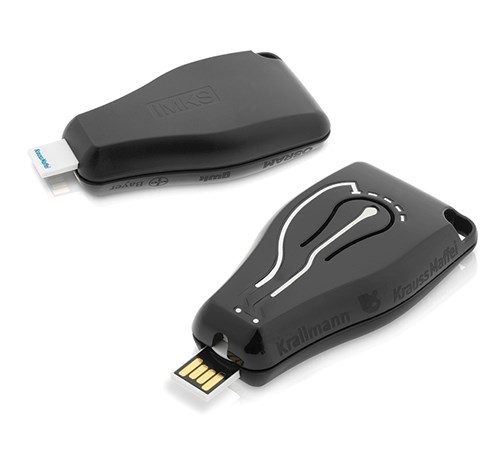
• Among the more unusual pairings, KraussMaffei operated a two-shot molding cell in which a first shot of polycarbonate was overmolded with molten zinc metal. The technology was developed by German molder and moldmaker Krallmann Group, which also built the small metal-injection unit on the side of the press. That unit melts a billet of zinc at 250 C and injects it through a special hot runner. Shot capacity is up to 30 g (at a density of 7.5 g/cc). In this case, only 3.5 g of metal was injected to show the capability of adding conductive paths or electrical contacts to a plastic part
• Arburg operated a cell in which a bead-foam molding press was integrated with an injection machine, using a six-axis robot to transfer foam components to the injection mold and to demold finished parts. The part was a socket consisting of a circular EPP foam part and a solid PP threaded component that was molded inside the foam piece.
According to Arburg, it’s not possible to achieve a permanent bond between the bead foam and solid PP without this overmolding process, which is called Particle-Foam Composite Injection Molding (PCIM). The photo opposite shows the part and how it can be incorporated into larger bead-foam components, represented in this case by an EPP board.
• Although less exotic, close coupling of a laser printer to an injection machine is not something you see every day. Boy Machines ran a cell in which laser printing was performed side by side with the injection press molding an ABS “business card.” The laser printer was integrated with the machine controls, where the print program was selected.
Related Content
Cobot Creates 'Cell Manufacturing Dream' for Thermoformer
Kal Plastics deploys Universal Robot trimming cobot for a fraction of the cost and lead time of a CNC machine, cuts trimming time nearly in half and reduces late shipments to under 1% — all while improving employee safety and growth opportunities.
Read More50 Years of Headlines … Almost
I was lucky to get an early look at many of the past half-century’s exciting developments in plastics. Here’s a selection.
Read MoreNew Technology Enables ‘Smart Drying’ Based on Resin Moisture
The ‘DryerGenie’ marries drying technology and input moisture measurement with a goal to putting an end to drying based on time.
Read MoreA Cost Saving Modular Approach to Resin Drying Automation
Whether implementing a moisture-sensing closed-loop system for a single dryer, or automating an entire plant, technology is available to take the guesswork and worry out of resin drying. Using a modular approach allows processors to start simple and build more capabilities over time.
Read MoreRead Next
Making the Circular Economy a Reality
Driven by brand owner demands and new worldwide legislation, the entire supply chain is working toward the shift to circularity, with some evidence the circular economy has already begun.
Read MoreFor PLASTICS' CEO Seaholm, NPE to Shine Light on Sustainability Successes
With advocacy, communication and sustainability as three main pillars, Seaholm leads a trade association to NPE that ‘is more active today than we have ever been.’
Read MoreRecycling Partners Collaborate to Eliminate Production Scrap Waste at NPE2024
A collaboration between show organizer PLASTICS, recycler CPR and size reduction experts WEIMA and Conair will seek to recover and recycle 100% of the parts produced at the show.
Read More























 (2).jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)