EPS Foam Manufacturer Molds On Despite Environmental Attacks
If plastic bags are Public Enemy No. 1 for environmental activists, EPS foam might be No. 1A, despite some very green credentials.
Over the past 40 years, a lot has changed at ACH Foam Technologies, an expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam manufacturer based in Denver. But one thing remains the same: the company’s commitment to recycling. For ACH Foam, and the majority EPS foam manufacturers, recycling has always been a key operational strategy, a fact often overlooked by EPS critics.
“We’ve been recycling since day one,” explains Frank Kiesecker, ACH’s Senior VP of Sales and Marketing. “It’s environmentally and economically the right thing to do.”
Today ACH is recycling more than ever, with recycled materials jumping from 4.1 to 5.4 million pounds over the last year. EPS has one of the highest recycling rates among all plastics: in 2012, 93.7 million pounds of both post-industrial and post-consumer EPS were recycled, and 127.3 million pounds of EPS were recycled in 2013.
“The numbers are pretty impressive when you consider that EPS is 98% air,” says Mary Burk, who works in corporate marketing for ACH.
At all of ACH’s facilities throughout the country, the company recycles 100% of its own production scrap, also known as post-industrial material. ACH also collects clean post-consumer EPS from the surrounding community.
“At ACH, we try to lead by example. We feel that EPS recycling is important to our global outlook, and we’re proud to offer our community additional recycling opportunities,” says Burk.
The closed loop recycling—along with the fact that EPS has a smaller environmental footprint than other competitive materials, is non-toxic and inert, and, despite some claims otherwise, doesn’t contain CFCs, HFC, HCFCs, or formaldehyde—is often ignored in the high-profile efforts to ban EPS. There will likely be more growth in EPS recycling as more companies follow the example set by Chick-Fil-A, Walmart, and Best Buy to begin corporate EPS recycling initiatives.
A Forest of Foam
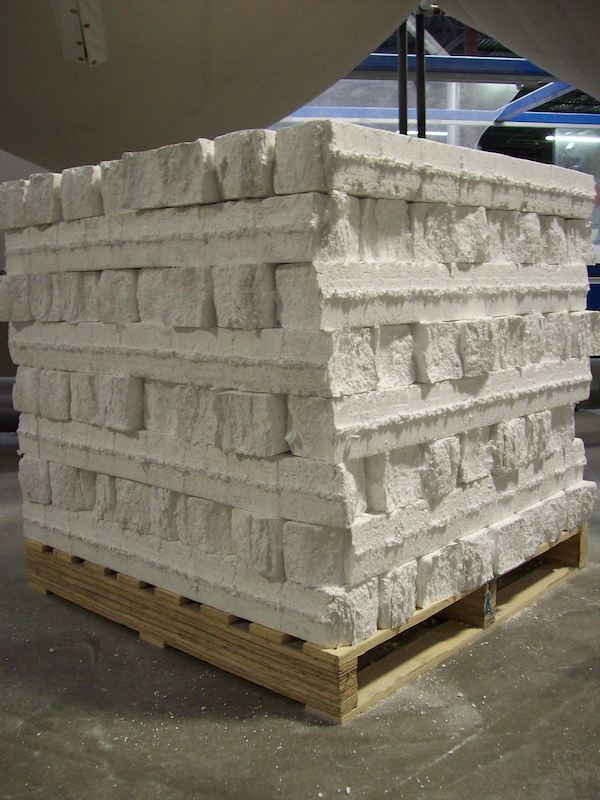
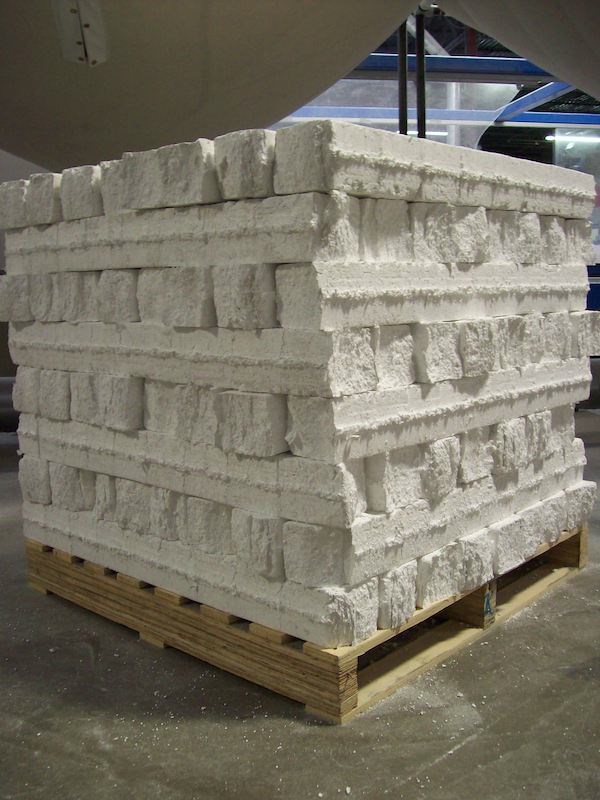
At ACH’s Denver plant, row after row of four-foot-square EPS blocks reaching 16 feet in the air tower over visitors. Handwritten information on each column details everything from the production date and weight of the EPS column to its density and percentage of recycled material.
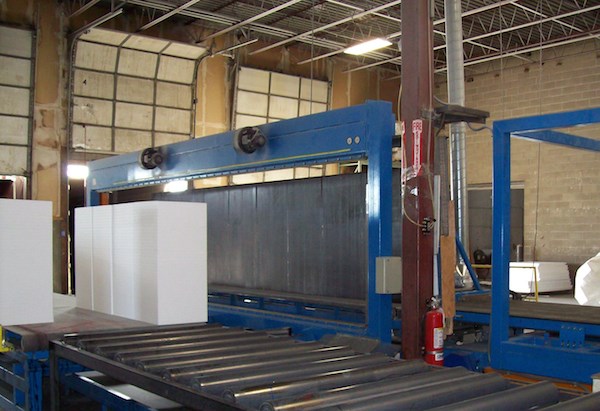
The blocks emerge from a vertical mold that looks like a large upright cabinet and stands nearly 25 feet tall. Material is fed into the top of the mold, and after a 4- to 10- minute cycle, depending on the product, the mold door swings open and the new block slides out along rollers towards a scale.
When the EPS first exits the mold, it’s not fully cured. Post mold, heat curing—done in special “heat rooms”—accelerates the drying process and creates dimensionally stable blocks. When asked how one moves the columns around from the mold to the curing room, an ACH worker responds dryly, “very carefully.” A modified dolly featuring longer forks at the bottom and at the back help workers maneuver the EPS monoliths.
Newly formed blocks are also subjected to a partial vacuum within the mold to speed up cooling. This added step pulls residual moisture from the block for a drier, better-fused product.
The peak production season for ACH, which has 400 total employees, runs from May through November. During that time, the Denver facility operates two shifts, six days a week. Kiesecker noted that despite the rows and rows of EPS blocks present during a recent tour, inventory was actually a little low. The facility generally tries to have several million board feet on hand.
From Beads to Foam
The EPS comes to ACH in small beads ranging from 0.5 to 1.3 mm in diameter. Kiesecker pulls a handful from a raw material bag and polystyrene resin runs through his fingers like grains of sand. Pre-expansion heats the beads so they release pentane gas and swell to almost 50 times their original size.
A computer-controlled weighing system actively manages how many beads are introduced into the expansion equipment. Next, steam and an agitator mixes the expanding beads. The heat of the steam causes pentane to be released. A level indicator notes when the specified volume has been reached. After a pressure-equalization phase, the expanded beads are moved into a bed dryer where all the condensed moisture is removed from the surface. The entire process takes approximately 200 seconds start to finish.
After drying, the expanded beads are “aged,” allowing them to fill back up with air and stabilize in a process that takes between 12 and 48 hours, depending on the desired density. Once this step is completed, the beads are ready to be molded into blocks.
EPS Bans Push Forward Unabated
Away from the bustling production floor looms proposed restrictions on EPS. In Denver, ACH’s hometown, the City Council was asked to consider a petition banning EPS. Supporters noted that cities like Portland, San Francisco, Oakland, and Berkeley have proven that a “Styrofoam ban is good for business, consumers and the environment.”
Petition signers added comments describing EPS as “despicable,” calling it “toxic waste” and stating that the proposed ban would “stop the waste landfill.” At ACH, however, the reality is that EPS is in high demand for recycled content insulation and packaging. Material that is not reused for new EPS products is densified and sent to a processor to be made into picture frames, hangers and even interior moldings.
“Right now, the supply of recycled foam is not keeping up with demand,” says ACH’s Burk. “There’s an incentive for would-be recycling entrepreneurs to change the debate.”
To learn more about EPS recycling, check out these links courtesy ACH:
EPS Industry Alliance – www.epspackaging.org
Dart Container’s Home for Foam – www.homeforfoam.com
ReFoamIt – www.refoamit.com
Waste to Waves – www.wastetowaves.com

Related Content
Gerdau Graphene Launches “First” Graphene-Enhanced PE Additive Masterbatch for Extruded Packaging and More
The company has also partnered with conglomerate Sumitomo Corp. for distribution of its graphene-enhanced masterbatches in Japan.
Read MoreNew Facility Refreshes Post-Consumer PP by Washing Out Additives, Contaminants
PureCycle prepares to scale up its novel solvent recycling approach as new facility nears completion.
Read MoreHow to Optimize Color Evaluation of Recycled Plastics
The right color measurement instrument and good working methods will minimize variability in color evaluation of PCR.
Read MoreRecycled Material Prices Show Stability Heading into 2023
After summer's steep drop, most prices leveled off in the second half.
Read MoreRead Next
Precision Processing Requires Precision Equipment
Moretto offers plastics processors and micromolders for a broad suite of auxiliary solutions targeted specifically for precision processing.
Read MoreLead the Conversation, Change the Conversation
Coverage of single-use plastics can be both misleading and demoralizing. Here are 10 tips for changing the perception of the plastics industry at your company and in your community.
Read MoreMaking the Circular Economy a Reality
Driven by brand owner demands and new worldwide legislation, the entire supply chain is working toward the shift to circularity, with some evidence the circular economy has already begun.
Read More