EXTRUSION: Effect of the Screw Flight On Melt Temperature, Energy Use
So-called rules of thumb regarding the design of flight clearance and width do not consider the temperature effect, both from the point of view of melt temperature and energy efficiency.
Most discussion of screw design is centered on the channel depths, or whether the screw has a barrier section, wave section, mixer, and so forth. You seldom hear much about the effect of the flight on the design. Out of convenience, flight width and clearance are usually chosen as approximately 10% of the screw diameter for the width and 0.1% of the diameter for the radial flight clearance. Screws smaller than 2 in. or larger than 10 in. may not follow that practice.
In general, the rule of thumb makes for an effective area for support of the screw in the barrel, a mechanically rugged flight, and sufficient pressure drop between channels to minimize backflow of melt as pressure develops. However, this generalization does not consider the temperature effect, both from the point of view of melt temperature and energy efficiency.
The shear of the polymer in the flight clearance can add significantly to the melt temperature and energy efficiency. The shear rate is described as Ÿ=DπN/h, where D is the diameter, N is the rev/sec, and h is the channel depth or flight clearance. For example, a 2.5-in. screw turning at 100 rpm (1.67 rps) with a channel depth of 0.100 in. and a flight clearance of 0.003 in. would have a shear rate of 131 sec-1 in the channel and 4372 sec-1 in the flight clearance.
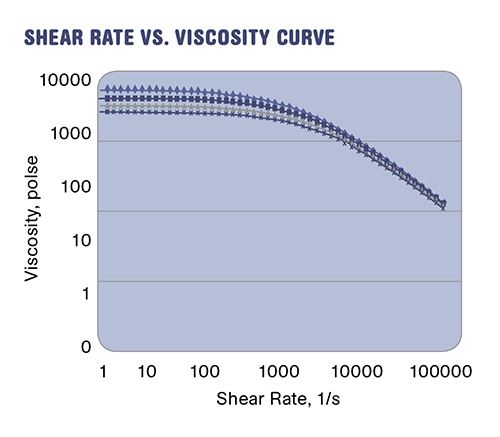
The shear rate/viscosity curve in accompanying graph shows a ratio in viscosity between the channel and the clearance of about 3.5:1 based on the calculated shear rates, with resulting viscosities being 3500 poise and 1000 poise for the channel and flight clearance, respectively.
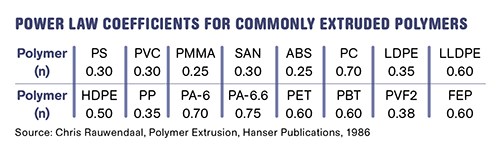
The greater the ratio or the greater the slope of the curve, the less effect that viscous dissipation will have in the clearance. The viscosity-thinning effect or the slope of the curve is typically described by the power law coefficient. This coefficient can range from 0.2 to 0.8 for common polymers, as shown in the accompanying table. The lower the number ,the more non-Newtonian the polymer and the more shear thinning will occur.
Because there is a relatively small amount of polymer in the flight clearance compared with the channel, the overall temperature rise due to the clearance is usually less than 20% of the total viscous dissipation for polymers having a power law coefficient less than 0.35. However, with long L/D screws, that can easily be exceeded. With polymers having a greater power law coefficient the viscous dissipation in the flight clearance becomes a significant design criterion and cannot be ignored.
Of course there are exceptions, even for polymers having a low power law coefficient, such as cooling screws, ultra-sensitive polymers, multiple-flighted screws, and mixing elements. Mixing elements in particular can have large areas with narrow clearances to the barrel that generate high levels of viscous dissipation. Regardless, recognition of the viscous dissipation effects in the flight clearance or mixing sections should be a part of all screw designs. Noted extrusion researchers Drs. Zehev Tadmor and Imrich Klein, in their book Engineering Principles of Plasticating Extrusion, have characterized the percentage of energy entering the extruder over the flight clearance as: (μf /µ) (H/W) (e/ δf), where: µ is viscosity in the channel; µf is viscosity in the clearance; H is channel depth; W is channel width; e is flight width; and δf is screw/barrel radial clearance.
This expression multiplies the ratio of the viscosity in the channel and flight clearance times the ratio of the depth to the width of each. This relationship takes into account the shear-thinning characteristics and depth-to-area relationship in the channel and clearance.
In addition to this relationship, the flight helix angle has a strong effect on the viscous dissipation in the clearance, primarily because it changes the channel width. Having shear rate/viscosity curves is essential for this analysis and many other aspects of screw design.
What does this mean to screw performance? Using the above analysis, it can be seen that the ratio of the flight width to the flight clearance is important; and from the chart it’s very important to know what the shear-thinning characteristics of the polymer are as depicted by the power law coefficient. The narrower the flights and wider the clearance, the less shear heating by viscous dissipation occurs over the flight. The lower the power law coefficient, the less the shear heating over the flight contributes to the overall energy going into the polymer.
For optimum screw performance with respect to energy going into the polymer, the flight width should be the minimum and the flight clearance the maximum for polymers having a higher power law coefficient.
This also relates to energy efficiency, since the shearing of the polymer in the flight clearance causes a rapid increase in its temperature. Although that polymer gets quickly mixed with the polymer in the channel, reducing its temperature and preventing degradation, it still adds to the overall melt temperature. Even though the polymer in the clearance gets quickly cooled as it exits the clearance, the temperature in the clearance is more or less permanent as the screw rotates.
The high temperature in the clearance transfers significant amounts of heat to the adjacent barrel, as it is much more (200 times) thermally conductive than the surrounding polymer. This causes barrel override and energy loss to the barrel cooling system, reducing power efficiency.
Naturally there are constraints to arbitrarily changing the flight width and clearance, but understanding and examining the effect can resolve many processing problems.
Related Content
How Polymer Melts in Single-Screw Extruders
Understanding how polymer melts in a single-screw extruder could help you optimize your screw design to eliminate defect-causing solid polymer fragments.
Read MoreWhy Are There No 'Universal' Screws for All Polymers?
There’s a simple answer: Because all plastics are not the same.
Read MoreTroubleshooting Screw and Barrel Wear in Extrusion
Extruder screws and barrels will wear over time. If you are seeing a reduction in specific rate and higher discharge temperatures, wear is the likely culprit.
Read MoreReduce Downtime and Scrap in the Blown Film Industry
The blown film sector now benefits from a tailored solution developed by Chem-Trend to preserve integrity of the bubble.
Read MoreRead Next
Lead the Conversation, Change the Conversation
Coverage of single-use plastics can be both misleading and demoralizing. Here are 10 tips for changing the perception of the plastics industry at your company and in your community.
Read MorePeople 4.0 – How to Get Buy-In from Your Staff for Industry 4.0 Systems
Implementing a production monitoring system as the foundation of a ‘smart factory’ is about integrating people with new technology as much as it is about integrating machines and computers. Here are tips from a company that has gone through the process.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)