Sheet Extrusion Line
A sheet extrusion line consists of an Extruder (single or twin screw), equipped with a Screen Changer and a Gear Pump, followed by a Static Mixer (sometimes feeding a Coextrusion Feedblock that is preceded by one or more additional extruders sets as described above), feeding a flat sheet die.
A sheet extrusion line consists of an Extruder (single or twin screw), equipped with a Screen Changer and a Gear Pump, followed by a Static Mixer (sometimes feeding a Coextrusion Feedblock that is preceded by one or more additional extruders sets as described above), feeding a flat sheet die.
The sheet is then cooled by a 3 (or more) roll stack (sheet take-off) with temperature, pressure and roll gap control.
Lastly the sheet is cut to length, wound into rolls or run inline into a secondary process

Extruder
The extruder is a machine consisting of a heated cylinder with an internal motor driven screw that plasticizes and pumps out the polymer.

Screen Changer
The screen changer is a more or less continuous device to filter impurities from the molten polymer in order to avoid shutting down the machine when the screen is full.
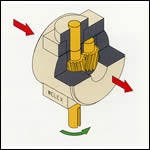
Gear Pump
A gear pump is a device including two intermeshing gears driven and rotating in a close fitting housing to provide precise volumetric output. It is usually run with an upstream pressure controller to maintain uniform input pressure from the extruder.

Static Mixer A static mixer is a mechanical housing that contains fixed vanes that break up the polymer flow into small streams before recombining them to homogenize the polymer flow for uniform melt viscosity prior to entering the die.

Coextrusion Feedblock
A coextrusion feed block is a device preceding a flat sheet or film extrusion die which combines the flow of several extruders with different materials into multiple uniform layers emerging from the die.

Flat Sheet Die
A flat (sometimes called T) sheet extrusion die is a heated distribution chamber to receive the uniformly molten polymer at a central entrance and extrude it through adjustable die lips into a flat exiting sheet of desired thickness. It may also include an internal adjustable restrictor (Choker) bar to assist in providing a uniform output across the entire width. The main transversal flow passage is called the manifold. It may have variable cross sections and tapers to assist in providing the uniform polymer distribution.
The lip opening may be adjusted manually via evenly spaced bolts or automatically via thermally expanded/contracted bolts controlled by a thickness gauging and control system.


Roll stack is a colloquialism for a sheet take-off, the three roll cooling system most commonly employed to cool sheet right after it comes out of the die. This is also sometimes called a calender which it also resembles.
The sheet take-off generally consists of three vertically oriented hardened chrome plated rolls, each with its own temperature controlled water (or other fluid in some higher temperature cases). These can be gang driven via a chain or individually driven. The middle roll is fixed in position while the outer two are pressure loaded via air or hydraulics against it.
The unit is usually run downstack for thinner sheet and upstack for thicker sheet. There are also inclined and offset roll versions, and others with additional non-contacting cooling rolls for higher cooling capacity.
Roll diameters depend on the required cooling capacity but range in the 12" to 36" (300-900mm) diameter range
Related Content
Bonding, Sintering Tech Advances Metal Bonding for Mold, Die Components
NPE2024: Punch Industry USA exhibits P-Bas, intended to replace the use of 3D printers when producing mold and die components, as well as a variety of mold component supplies.
Read MoreIs Your Die Flow Changing Despite Following All the Correct Formulas?
Maybe the problem is that you're starting up with a dry die. Here are tips to solve this issue.
Read MoreCrosshead Die for Elastomers Adjusts Easily
NPE2024: Mechanically actuated gum space adjustment requires only ordinary socket wrench.
Read MoreMedical Tubing: Use Simulation to Troubleshoot, Optimize Processing & Dies
Extrusion simulations can be useful in anticipating issues and running “what-if” scenarios to size extruders and design dies for extrusion projects. It should be used at early stages of any project to avoid trial and error and remaking tooling.
Read MoreRead Next
Beyond Prototypes: 8 Ways the Plastics Industry Is Using 3D Printing
Plastics processors are finding applications for 3D printing around the plant and across the supply chain. Here are 8 examples to look for at NPE2024.
Read MoreFor PLASTICS' CEO Seaholm, NPE to Shine Light on Sustainability Successes
With advocacy, communication and sustainability as three main pillars, Seaholm leads a trade association to NPE that ‘is more active today than we have ever been.’
Read More