Novel Materials for High-Pressure Composite Hydrogen Storage Tanks
DSM is aiming its technology for CNG tanks to hydrogen storage tanks for transportation and more.
Lightweighting in automotive and other industries along with the drive to alternative fuels that outperform conventional fuel in energy efficiency and CO2 emissions reduction are key drivers for the latest materials development from Royal DSM (U.S. office DSM Engineering Plastics North America, Troy, Mich.).
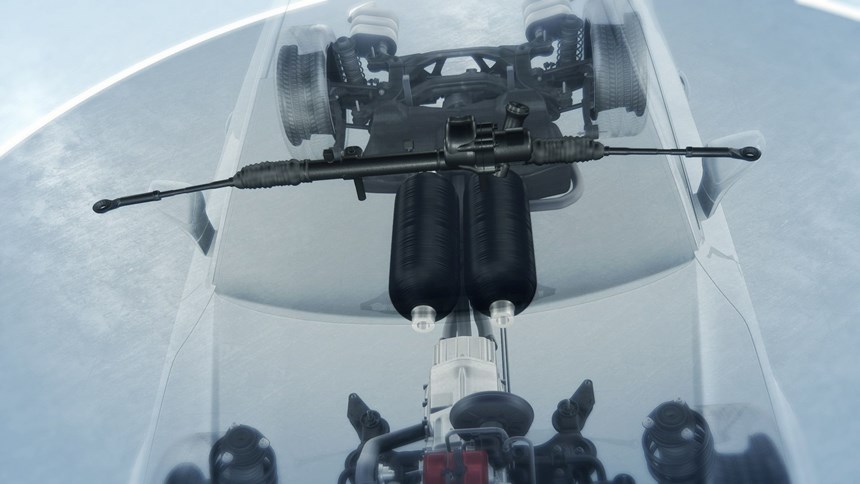
The company has proposed a materials solution for high-pressure composite tanks for hydrogen storage. “We had already developed this technology for compressed natural gas (CNG) tanks, and now we are testing the same material and design principles for hydrogen tanks to meet the needs of the automotive industry,” notes application development engineer Bert Keestra.
Hydrogen has the highest energy per mass of any fuel. One kg of hydrogen is equivalent to 33.3 kWh, which means it delivers three times more energy than conventional fuel. But hydrogen’s low ambient temperature density results in a low energy per unit volume. This requires the development of advanced storage methods that have the potential for higher energy density. DSM sees the hydrogen tanks as the next step in fuel storage, as such storage is a key enabling technology for advancing hydrogen and fuel cell technologies in applications that include stationary power, portable power and transportation.
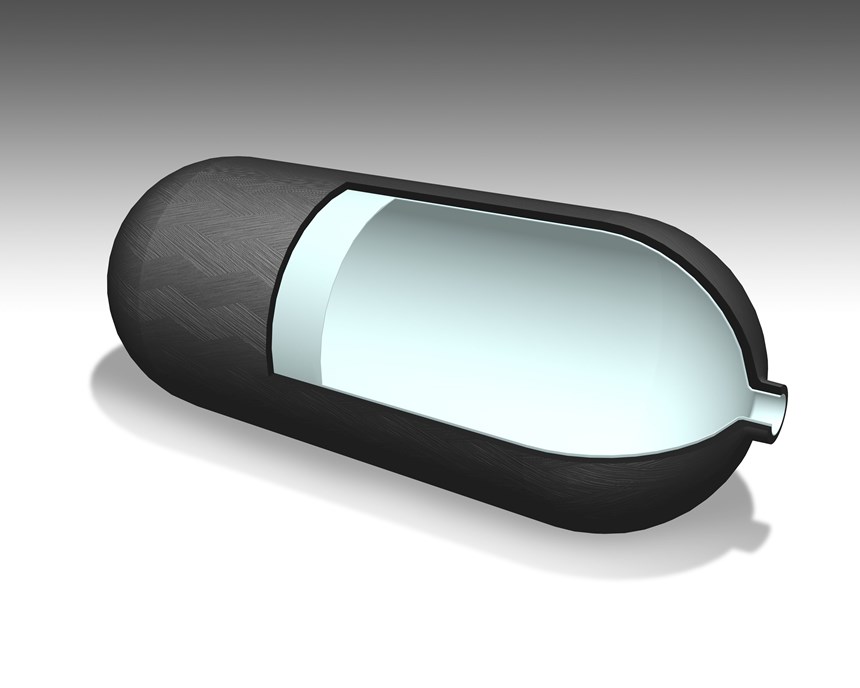
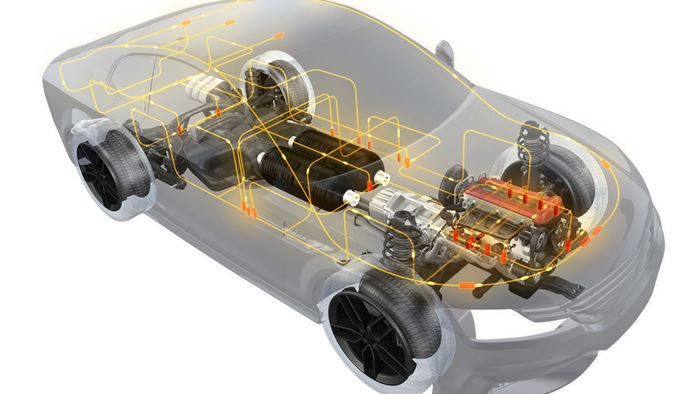
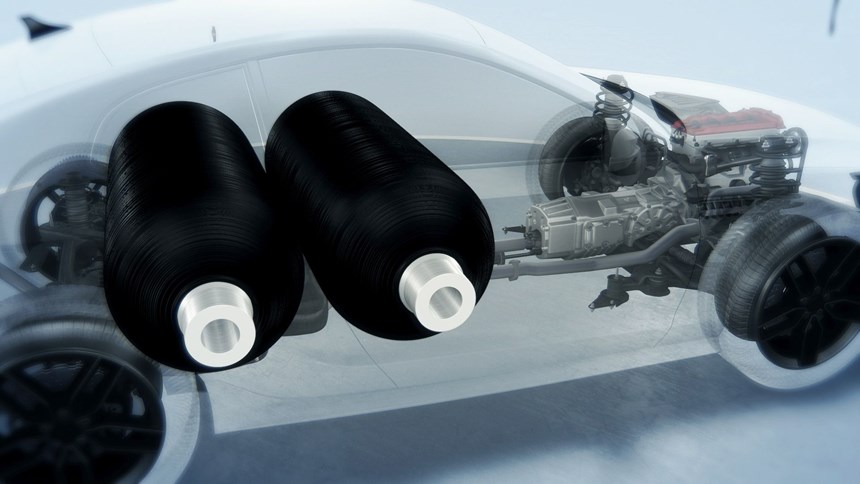
DSM’s two-part tank design features a proven, blow molded liner made of Akulon Fuel Lock, a nylon 6-based plastic with a very high barrier to hydrocarbons. The tank can then be potentially further reinforced by wrapping it in unidirectional (UD) continuous fiber-reinforced thermoplastic tapes made of EcoPaXX nylon 410. This combination of commercially available materials reportedly has already proven to be very effective in CNG tanks, and DSM is now actively testing the concept in hydrogen tanks.
According to the company, the result would be the lightest-weight plastic tank available for hydrogen storage applications. Reducing weight is key—since every 10 kg removed from a vehicle translates roughly into a reduction in carbon dioxide emissions from the vehicle on the road of one gram per km.
For the liner, Akulon Fuel Lock nylon 6-based resin is said to greatly reduce weight compared to metal, while also offing improved permeation versus polyolefin liners, meaning that the gas stays in the tank. The liner material, which is 100% recyclable, is reportedly safe with no debuckling. Moreover, this material is optimized to remain ductile and tough, even at extremely low temperatures (-40 C). This was important for CNG, but is even more crucial for hydrogen storage, as the working pressures are much higher.
Related Content
-
Automotive Awards Highlight ‘Firsts,’ Emerging Technologies
Annual SPE event recognizes sustainability as a major theme.
-
General Polymers Thermoplastics to Further Expand Distribution Business
NPE2024: Following the company’s recent partnership buyout, new North American geographic territories are in its sight.
-
Prices of Volume Resins Drop--Except for PE
The downward trajectory appears to be continuing into the first quarter for most resin prices, though PE and possibly PP may remain somewhat stable.