What Is the Right Plastics Joining Process for You: Part 3—Coolant Manifold Case Study
What is the most appropriate plastics joining solution for a 30% glass-filled nylon coolant manifold?
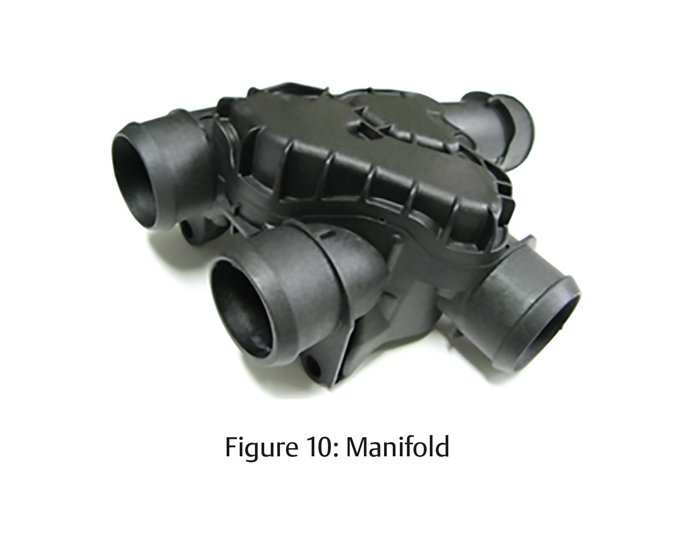
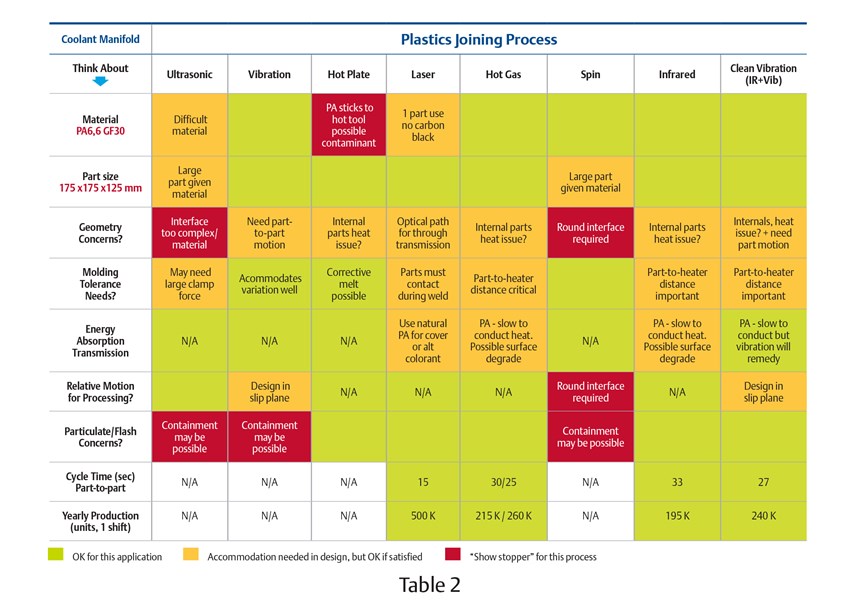
To illustrate the process of determining the most appropriate plastics joining solution for a particular application, consider the coolant manifold shown in Fig. 10 above. Assume for a moment that the part shape has yet to be finalized and that the following information is known:
● Required Material: PA66 GF30
● Part Size: 175 mm x 175 mm x 125 mm
● Production Volume: approximately 175,000/yr
Special requirements include: Strict avoidance of particulate break-off inside the part that would contaminate fluid. Hermetic seal. Burst pressure of 14 bar (200 psig) minimum.
Table 2 demonstrates a decision matrix of relevant points to consider in the left column with color codes in each column indicating whether the corresponding joining technology is viable. In addition to color coding, select comments are included in certain areas for clarification.
The analysis shows four viable processes, given the design requirements as long as the comments in yellow boxes are satisfied. Material testing should be done with any process considered to further vet out any challenges. A plastics joining equipment supplier should have lab equipment to test each process and be willing to weld test samples and assist with weld strength testing to help in the optimization process.
If multiple processes are able to meet the requirements, as in the example above, production criteria also need to be considered. The four viable processes all meet the yearly capacity requirement, so a number of production considerations like these can help focus the selection:
● What is the capital budget for the program versus the cost of equipment needed?
● Is the take outt time of the process consistent with the production plan?
● If one process is much faster than needed, is there another application that can be run in the same machine?
● If more capacity is desired (say for safety stock production) is a multi-cavity tool
an option?
For optimum results, it is important to not make a technology decision based on whether your company has experience with an appropriate technology. Being open to new technologies and methods helps ensure the most effective solution gets chosen.
In summary, four overarching considerations can guide you to determining the best plastics joining technology for your application, and thus help you achieve success in solving the tough challenges the automotive industry faces.
- Maintain a solid understanding of the latest advancements in plastics joining technologies and polymer science.
- Maintain a “process neutral” approach and consider a variety of joining technologies during the design phase. Be open to using whatever is shown to be the most effective solution for your application.
- Evaluate the key variables that will determine your best solution, including material to be used, size and complexity of part design, production volume/cycle time, weld cleanliness and aesthetics, and expertise and support of equipment suppliers.
- Involve all stakeholders early in the design process, including resin suppliers and processing equipment suppliers.
Read Part 1: What Is the Right Plastics Joining Process for You?
Read Part 2: Available Plastics Joining Technologies
About the author: Craig Birrittella holds the position at Emerson as Automotive Segment Manager, Americas, for Branson Ultrasonics, Danbury, Conn. Graduating from State University of New York at Buffalo with a mechanical engineering degree, Craig holds a patent related to using a lens to adapt laser intensity for uniform welding. Emerson is a global manufacturer of Branson Ultrasonics material joining and precision processing equipment. He can be contacted at Craig.Birrittella@Emerson.com.
Related Content
New Concept for HDPE Paint Pails With Plasma Coating, Digital Printing
NPE2024: Delta Engineering presented integrated systems for injection molding, barrier coating and printing HDPE paint pails.
Read MoreA Guide to Ultrasonic Welding Controls
Ultrasonic welding today is a sophisticated process that offers numerous features for precise control. Choosing from among all these options can be daunting; but this guide will help you make sense of your control features so you can approach your next welding project with the confidence of getting good results.
Read MoreThin Wall Ultrasonic Bonding Technology for Automotive
NPE2024: Dukane’s new Ultrasonic Thin Wall welding system is well suited for welding applications of PP to PP TD25 painted parts.
Read MoreAdvanced Inspection of Bottles and Labels
NPE2024: Intravis shows new system for full label inspection on round, randomly oriented bottles; and redesigned bottle inspection system with more modular design.
Read MoreRead Next
What Is the Right Plastics Joining Process for You? Part 1
Changing demands, advancing technology and a process-neutral approach to plastics joining for under-the-hood automotive parts.
Read MoreWhat Is the Right Plastics Joining Process for You: Part 2—Available Technologies
The four primary joining technologies—vibration, clean vibration, infrared, hot-gas/convection—offer different benefits and challenges for different applications.
Read MoreMaking the Circular Economy a Reality
Driven by brand owner demands and new worldwide legislation, the entire supply chain is working toward the shift to circularity, with some evidence the circular economy has already begun.
Read More