When choosing feeders for a compounding line, do you know the materials’ particle sizes and shapes? Bulk densities? Flow characteristics (free-flowing or not)? Throughput and accuracy requirements for each feeder? That’s just a sample of the questions to ask beforehand.
(Photo: Orbetron, LLC)
Processors in the market for feeding equipment have a number of options to consider when choosing the correct feeder for their application. One of the most important factors in making the best choice is understanding the range of materials you intend to feed with this equipment. Here are some basic questions to ask about materials and other parameters when evaluating feeder technologies and discussing options with your equipment suppliers:
• Is the feeder designed to handle the required feed rates?
• Is the material you are choosing able to achieve your accuracy and feeding requirements?
• Is the feeder designed to fit into the space required?
• Will it be a volumetric or gravimetric feeder?
• Can the feeder handle all of the materials planned, or do changes have to be made for the feeder to work correctly?
Investing in the correct feeder technology will help your ROI and product stability. Create a relationship with your equipment suppliers and evaluate the best solution for your process. The more information you know about your material the easier it is to choose the correct feeder.
“The more information you have on your material, the easier it is to choose the correct feeder.”
Materials Characteristics for Feeding
Once you and your material supplier have decided on the type of materials that work best with your process bring your feeding equipment supplier in to evaluate the material that you plan to use and the process for which it is intended.
• What are the different shapes and sizes of raw materials that you will be processing? Samples of each material will be required.
• What is the bulk density of each material?
• What unique flow characteristics does each material have? These are typically designated as free-flowing, fairly free flowing, and non-free flowing
• At what temperature will you be processing each material? For example, PET is typically dried at a high temperature and may require special nozzles for warm air or other options.
• What are the throughput requirements for each material? Be prepared to specify minimum, maximum and nominal rates.
• What is the area of classification? Be sure to advise your equipment supplier if material is volatile or in a volatile area. Please review and supply the MSDS information so your equipment suppliers will understand how to handle the material when testing.
• What are your accuracy requirements? Feeding equipment suppliers are challenged in finding the best feeder technology recommendation to achieve your accuracy and throughput requirements. This may sound like a simple task; but in reality, if you do not implement the correct feeding technology you will end up spending money, time and resources chasing problems that could have been discovered in lab tests.
Let’s dive into a few examples of customer requirements and which considerations were necessary to achieve their goals. These examples of materials were considered for a single-component feeding system or as part of a multi-component feeding system.
Matching accuracy and throughput requirements can be a significant challenge to feeder design and selection.
Example 1: Feeding a proprietary pellet

FIG 1 A special disc feeder was required for a clear pelletized material with a range of particle sizes, varying bulk density, and high accuracy requirements at very low throughput (0.51 g over 15 sec — the amount shown in the weigh scale).
(Photo: Orbetron, LLC)
A clear pelletized material has a bulk density of 40 lb/ft3. The material size varied from 17 mm to a small crystal the size of salt. The customer required a feed rate of 0.275 lb/hr or 125 g/hr.
In reviewing the above information, the biggest issue with the material was the pe. By just a visual review, a standard auger feeder would not achieve the proper consistency needed for the low feed rate. We opted for a special disc feeder with a reduced disc size to allow the longer pellet sizes to be fed consistently.
As expected, the bulk density varied but was able to be fed within a few tenths of a gram variation over a 15-sec time period. To improve accuracy, we recommended to the customer that the material be granulated or cut more evenly. Flowability was not an issue; but, as would be expected, the smaller fines fell to the bottom of the feed hopper first and caused the feed rate to change greater than required over time.
The desired throughput was easily achieved using the disc feeder designed for low rates. Figure 1 shows the amount (0.51 g) required in 15 sec.
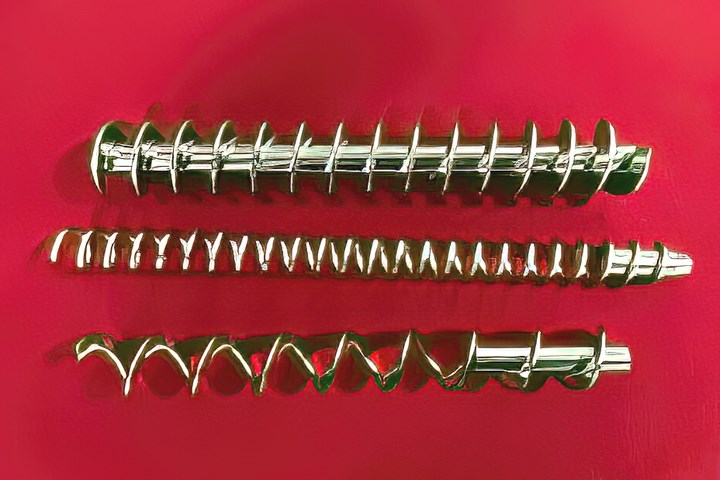

FIG 2 Widely varying bulk densities of regrind materials may require a variety of feeder screws. (Photo: Orbetron, LLC)
Example 2: Feeding Regrind
There is a push for processors to utilize more and more regrind in their products. Those who do not produce enough in-house regrind look for outside sources of regrinds through brokers, recyclers and compounders. The challenge is to ensure how consistently they can feed the different regrind shapes, sizes, and bulk-density variations. Here is where the equipment manufacturer can help with designing the correct feeder configuration.
Most common issues that processors will deal with is how much regrind can be introduced into their process before it starts producing a bad product. This typically requires an evaluation of the regrind and establishing a proper feeder screw design and tube diameter.
Regrinds present special feeding challenges in terms of bulk density and consistency.
These are some basic concepts you can consider when feeding regrind-based material. It is always beneficial to work with your feeder supplier to evaluate the best feeder for you process.
• Larger chunks of regrind typically will require the ID of the tube to be greater than the screw diameter to prevent the feeder from locking up. Depending on the type of material (such as higher bulk densities), those larger chunks may require a solid-core auger for more consistent transportation through the flights.
• For lower density regrinds a spiral screw may be better suited.
• With regrinds, be prepared to use multiple screws and designs to achieve your different throughput rates (Fig. 2).
• If lighter regrinds are introduced back into your process, internal feeder and or hopper agitation may be necessary to eliminate bridging.
• Keep the inlet to your auger screw as large as possible; this will help keep material from bridging.
• With some regrind materials, using downcomer designs can create periodic material stoppages, so it will be important to understand flowability and design equipment accordingly.
Example 3: Feeding Antioxidant Additive

FIG 3 A special disc design was required to feed this additive powder/flake material without working the material, which caused it to harden and stop flowing.
(Photo: Orbetron, LLC)
It was required to feed an additive in powder/flake form at 5 to 10 lb/hr with a 33 lb/ft3 bulk density. This particular additive (Fig. 3) behaves unusually in feeding. In the initial review, it flowed fairly well and seemed like an easy material to feed, but over time it proved to play havoc with a feeder. When testing this material over a couple days using a vibratory, single- or twin-screw feeder, the material would start to harden in the area where the material was worked constantly. The eventual outcome would be reduced flow and/or stoppage of the feeder. This reduced flow would cause the user to shut down the process regularly to clean the feeder.
The processor wanted to find a feeding technology to reduce his downtime. After further testing and evaluation, we designed a special disc design that allowed the material to flow with very little working between the material and metal surface of the feeder. To improve accuracy, we utilized a gearmotor that would run at a low rpm. Utilizing this concept, we were able to reduce the cleaning time and number of times cleaning was required.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Roger Hultquist is co-owner and president of Orbetron, LLC in Lincoln, R.I., a manufacturer since 2011 of bulk material feeders for quantities from 1 g/hr up to 20,000 lb/hr. He has been involved in the bulk material and liquid feeding industry for over 35 years, working for a number of different auxiliary equipment manufacturers that supply to industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, plastics and chemicals.
Related Content
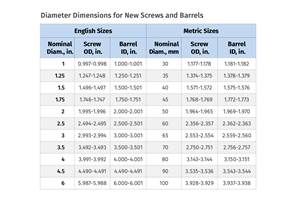
Troubleshooting Screw and Barrel Wear in Extrusion
Extruder screws and barrels will wear over time. If you are seeing a reduction in specific rate and higher discharge temperatures, wear is the likely culprit.
Read MorePart 2 Medical Tubing: Use Simulation to Troubleshoot, Optimize Processing & Dies
Simulation can determine whether a die has regions of low shear rate and shear stress on the metal surface where the polymer would ultimately degrade, and can help processors design dies better suited for their projects.
Read MoreMedical Tubing: Use Simulation to Troubleshoot, Optimize Processing & Dies
Extrusion simulations can be useful in anticipating issues and running “what-if” scenarios to size extruders and design dies for extrusion projects. It should be used at early stages of any project to avoid trial and error and remaking tooling.
Read MoreUse Interactive Production Scheduling to Improve Your Plant's Efficiencies
When evaluating ERP solutions, consider the power of interactive production scheduling to effectively plan and allocate primary and secondary equipment, materials and resources on the overall production capacity of the business and conclude that this is a key area that cannot be overlooked.
Read MoreRead Next
Take Proper Care in Feeding Your Extruder
Everything that happens in an extruder starts at the feed throat, so proper attention to that zone’s temperature pays off in quality and productivity.
Read MoreThe Path to Pellet Perfection
In underwater pelletizing, numerous variables in the equipment, process and material affect pellet shape, consistency and quality factors such as fines. Defining the “perfect” pellet depends on the conditions of end use, and achieving that ideal requires understanding of the causes of imperfections.
Read MorePeople 4.0 – How to Get Buy-In from Your Staff for Industry 4.0 Systems
Implementing a production monitoring system as the foundation of a ‘smart factory’ is about integrating people with new technology as much as it is about integrating machines and computers. Here are tips from a company that has gone through the process.
Read More