Lockheed Martin Works with MakerBot for its AI-Assisted Lunar Rover Project for NASA
MakerBot 3D printers have been in use for about five years and have provided easily accessible 3D printing for a host of projects for Lockheed Martin’s team of engineers.
MakerBot, a Stratasys company, announced that Lockheed Martin has extended its use of MakerBot 3D printers to produce parts and designs for its upcoming space projects.
In alliance with General Motors, Lockheed Martin is developing a new fully-autonomous lunar rover that could be used for NASA’s Artemis program.
Some elements of the rover’s autonomy system’s early design and development are done at Lockheed Martin’s R&D facility in Palo Alto, Calif., the Advanced Technology Center (ATC), which is well-equipped with a variety of technology, including a lab full of 3D printers.
The latest addition to the ATC’s 3D printing lab is the MakerBot METHOD X 3D printing platform. With METHOD X, the team can print parts in materials like nylon carbon fiber and ABS giving them the performance they need for accurate testing—and due to METHOD X’s heated chamber, the parts are dimensionally accurate without the variable warping that comes with a typical desktop 3D printer.
“At ATC, we have multiple MakerBot printers that help with quick turnaround times,” said Aaron Christian, senior mechanical engineer, Lockheed Martin Space. “I will design a part, print it, and have it in my hand hours later. This allows me to quickly test the 3D-printed part, identify weak points, adjust the model, send it back to print overnight, and then have the next iteration in the morning. 3D printing lets me do fast and iterative design, reducing wait times for a part from weeks to hours.”
Lockheed Martin engineers are testing a multitude of applications designed for the lunar rover. Christian and his teammates are using METHOD X to print a number of parts for prototyping and proof of concept for the rover project, including embedded systems housing, sensor mounts, and other custom parts. "The MakerBot METHOD X produces dimensionally tolerant parts right out of the box – and for all sorts of projects, you can print multiple parts that can mate together."
Many of these parts are printed in MakerBot ABS and designed to withstand desert heat, UV exposure, moisture, and other environmental conditions. In combination with Stratasys SR-30 soluble supports, parts printed with MakerBot ABS are designed to provide a smoother surface finish compared to breakaway supports. Printing with dissolvable supports also enables more organic shapes that would have been otherwise impossible to produce through traditional machining.
“We’re in the very early stages of development and the rover we have at ATC is a testbed that we designed and developed in-house. This affordable modular testbed allows us to make quick changes using 3D printing to change the design for other applications, whether it be military, search and rescue, nuclear applications and just extreme environment autonomy needs,” Christian said.
3D printing lets the team test parts affordably, iteratively, and modularly. One of the parts printed for the rover was a mount for a LIDAR, a sensor that can help determine the proximity of objects around it. Broadly used in self-driving vehicles, Lockheed Martin uses LIDAR in a lot of its autonomy projects. The mount was designed to sit on the rover, a completely modular robot system, so it was printed in ABS which allows it to handle more extreme conditions than typical PLA. The mount also allows engineers to continuously swap out the LIDAR with different sensors, such as a stereo camera, direction antenna, RGB camera, or a rangefinder. It has a complex organic shape to it, which can be difficult to achieve via traditional machining. The mount also has a lot of access to ensure proper airflow to keep the part cool and temperature-regulated on the robots.
The embedded electronics housing is designed to go inside the rover or in other robots at the ATC. The housing was developed to protect the electronics from anything that could potentially fall on them. Although it was printed in PLA, due to its hexagonal shape, it offers solid strength. Its design also lends itself well to the open airflow needed to cool down the system while still protecting the device.
In addition to printing prototypes, Lockheed Martin is using 3D printing for production parts that will go into various space-going platforms.
“A big advantage for testing and flying 3D-printed parts for space applications is that it simplifies the design. You can create more complex shapes. It reduces the number of fasteners needed and part count, which is a huge cost savings because that’s one less part that has to be tested or assembled,” noted Christian. “This also opens up for future in-situ assembly in space. You have designed, printed, and tested the part on Earth. Now you know that, in the future, you can 3D print that same part in space because you have shown that the material and part work there.”
Manufacturing in space is expensive but appealing for future applications and missions. Now, bulk materials can be flown into space to be used to 3D print multiple parts and structures, rather than flying each part out individually. Combining that with a digital inventory of part files, 3D printing in space reduces costs by cutting out the need for storage and multiple trips, which make it expensive to fly.
“The digital inventory concept helps push our digital transformation forward—you have digital designs that you can ship up, where you just print the parts and have them assembled on location,” Christian said.
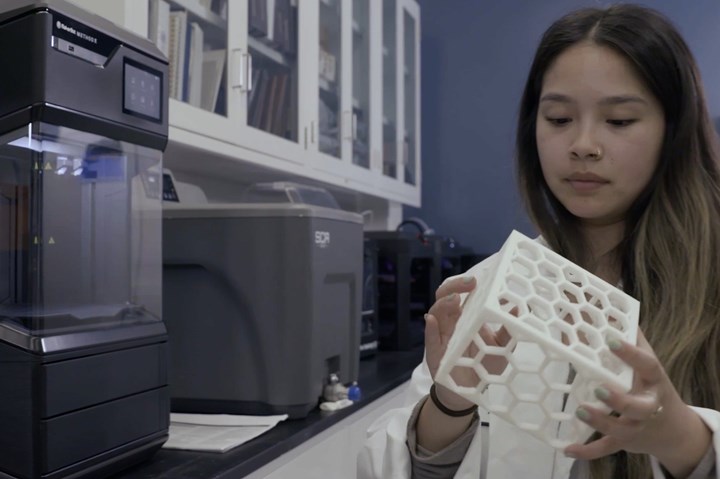

Lockheed Martin Research Engineer Alyssa Ruiz inspects a 3D printed electronics housing printed on METHOD X in the ATC's 3D printing lab.
Related Content
Production Tool, Prototype Time
Mantle's metal 3D printing technology targeted toolmaking and injection molders and moldmakers are taking notice.
Read MoreBusiness Slowing? There's Still Plenty of Stuff to Do
There are things you may have put off when you were occupied with shipping parts to customers. Maybe it’s time to put some of them on the front burner.
Read MoreDuPont Buys Medical Product Manufacturer Spectrum Plastics
Purchase price of $1.75 billion for leading supplier of extruded, molded, and 3D printed medical components.
Read MoreAdditive Technologies for Injection Mold Tooling Ride Tailwinds
NPE2024: Lowering barriers to additive manufacturing adoption in toolmaking.
Read MoreRead Next
System to recycle waste into 3D-printed filament to use in space
Tethers’ Positrusion recycler will turn plastic waste on the International Space Station (ISS) into high-quality 3D-printed filament.
Read MoreStratasys Coalition Expands to Ramp Up Face Shield Production With 3D Printing
Stratasys has received requests for 350,000 face shields, so further acceleration in production across coalition members is critical.
Read MoreSpace: Where 3D Printing Innovates?
It’s called the “Final Frontier” but maybe space is actually a closer to a present-day trendsetter. What does that mean?
Read More