50 Years...600 Issues...and Still Counting
Matt Naitove marks his first half-century in plastics reporting, with a few of his favorite headlines.
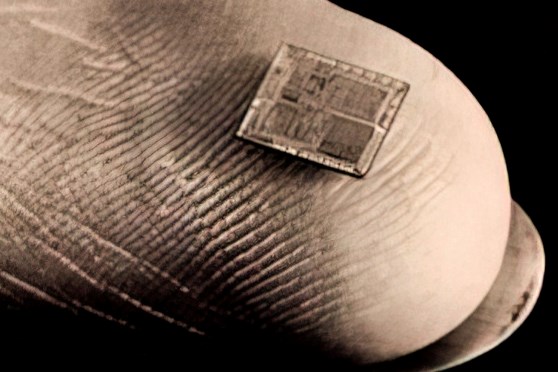
An early “scoop” of Matt’s was a 1975 report on the first use of a microprocessor in plastics machinery controls—for, of all things, a filament winder for composites.
Editor’s Note: This issue of Plastics Technology marks Matt Naitove’s 50th anniversary as part of the editorial team. That’s 600 issues. In honor of his commitment to the publication, the industry and to editorial excellence, it is my honor to turn this page over to him this month so that he can reflect on all that he has seen—and reported on—over the past half century.
Jim Callari
When I started at PT as an assistant editor in July of 1972, I was given a desk in a hallway with a telephone, a typewriter and a tall stack of press releases. The managing editor told me, “When you get to the bottom of that pile, come ask for more.” It proved to be a comprehensive introduction to the plastics industry, because those random press releases covered every conceivable subject—primary machinery, auxiliaries, tooling, components, resins and additives. A lot of people patiently and generously took my phone calls asking why such-and-such innovation or modification made this-or-that product more productive, efficient or easier to use.
I eventually graduated from that hallway desk to my own office, and from press releases to field reporting inside actual production plants. I had the privilege to witness, and report on, so many exciting new technologies in the intervening 50 years. Here are few favorites that stick in my memory:
• The “unforgettable” plastic: In 1981, a press release landed on my desk announcing the commercialization of a new plastic called “PEEK” (short for polyetheretherketone). A name like that has got to stick in your mind. First reaction: What a cute name! Second reaction: What a heck of an engineering material! In the 1980s and ’90s I attended the public launches of several other new materials—DuPont’s Rynite PET, Eastman’s PETG, Shell’s Carilon polyketone, and Dow’s mLLDPE. I also recall being introduced to the wonders of thermoplastic elastomers, courtesy of Uniroyal’s TPR and Monsanto’s Santoprene (both TPVs).
• The first microprocessor in plastics: I traveled to Wisconsin in the fall of 1975 to see this new development in electronics, a subject I knew nothing about, for controlling plastics machinery. This tiny chip that fitted in the palm of your hand could replace a whole cabinet full of wires and cables. It had a name that kind of made sense: a microprocessor. It sounded so smart that it would probably catch on. By 1980 every maker of plastics controls was proclaiming they had a microprocessor! Guess what sort of plastics equipment it was first used on? A filament winder for fiberglass composites.
• Debut of all-electric injection machines: I missed the actual debut back in the 1960s, when Battenfeld floated the idea, but it didn’t take. The time was right, however, in 1984, when I was lucky to make my first visit to a Japanese plastics fair. And there they were: commercial all-electric injection presses from Nissei and prototypes from Niigata. They were only 5 and 10 tons, but I’ve seen very few ideas in plastics picked up so widely and enthusiastically in such a short time.
• Plastics made by “bugs”: I was first introduced to biopolymers—biologically produced by microbial fermentation—by representatives of Coors Brewing Co. back in the early 1980s. Grain could be fermented into not just beverages, but also plastics! Who knew? The Coors exploration of this technology petered out soon, but I was reintroduced to the subject by ICI in England, whose aptly named Biopol resin ended up with the late lamented Metabolix. And of course, Cargill and Dow entered the market with PLA. Their venture became NatureWorks.
• Mold-filling simulation: Originally it was called mold analysis, or just Moldflow, the name of the Australian academic spinoff venture that did the most to popularize the concept. Moldflow was launched in 1978, but I dug into it and wrote the first feature-length article about it in this magazine in 1984. I followed the development of the technology eagerly thereafter—other editors were satisfied to leave this “techy” topic in my hands for at least the next decade.
• “Smart manufacturing”: I’ll end with one of the biggest and most far-reaching trends that is grabbing a lot of headlines today—Industry 4.0, also variously known as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIOT), digitalization, or the coming era of “smart factories.” I’m pleased to say that Plastics Technology caught on to this trend way back before it became fashionable—in the 1980s, in fact. We began pounding the drum editorially for what was then called “computer-integrated manufacturing,” or CIM. We began an annual CIM Leaders Awards competition in 1986, which ran through 1998. By then we got the feeling that CIM had lost its sense of novelty. Fast-forward to the K 2016 show in Düsseldorf, when CIM re-emerged as a prominent industry theme—this time under the moniker “Industry 4.0.” It has been nearly inescapable since then.
Related Content
Back to Basics on Mold Venting (Part 1)
Here’s what you need to know to improve the quality of your parts and to protect your molds.
Read MoreProcess Monitoring or Production Monitoring—Why Not Both?
Molders looking to both monitor an injection molding process effectively and manage production can definitely do both with tools available today, but the question is how best to tackle these twin challenges.
Read MoreInjection Molding: Focus on these Seven Areas to Set a Preventive Maintenance Schedule
Performing fundamental maintenance inspections frequently assures press longevity and process stability. Here’s a checklist to help you stay on top of seven key systems.
Read MoreBack to Basics on Mold Venting (Part 2: Shape, Dimensions, Details)
Here’s how to get the most out of your stationary mold vents.
Read MoreRead Next
Lead the Conversation, Change the Conversation
Coverage of single-use plastics can be both misleading and demoralizing. Here are 10 tips for changing the perception of the plastics industry at your company and in your community.
Read MoreFor PLASTICS' CEO Seaholm, NPE to Shine Light on Sustainability Successes
With advocacy, communication and sustainability as three main pillars, Seaholm leads a trade association to NPE that ‘is more active today than we have ever been.’
Read More