Cooling Bore Creates Turbulent Flow
Hasco says its Cooling Tornado facilitates turbulent flow, boosting cooling effectiveness by up to 20%.
Hasco says its new Z9665/… Cooling Tornado cooling bore increases efficiency and saves energy during mold cooling by promoting turbulent flow of the cooling medium. Used in combination with runners in core cooling systems and directly in the corresponding cooling bores, the Cooling Tornado Z9665/.... produces turbulent flow to increase the cooling effectiveness by up to 20%, according to Hasco, depending on the flow L/min. By interrupting the laminar lower layer of the cooling medium, this turbulence enables the inner core of the cooling medium to flow to the outer sheath and considerably improve the heat transfer.

Hasco says its Z9665/… Cooling Tornado creates turbulent flow for more effective mold cooling.
Source: Hasco
Compared with conventional cooling bores, Hasco says temperature differences of up to 10°C can be attained with the Cooling Tornado, enabling potential energy savings between 20 and 40%. The Cooling Tornado can be retrofitted into existing systems with customized lengths possible.
In terms of installation, the Cooling Tornado is positioned and fixed at the end of a cooling channel via a clamping ring. The mounting can both be carried out in combination with cooling pipes for core cooling and also directly mounted in the cooling bores.
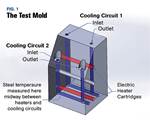
Hasco says testing showed that in a comparison of the cooling circuits with and without the use of the Cooling Tornado, a surface temperature reduction of 10% was measured. Using a flow rate of 6 L/min, Hasco says the surface temperature of the cavity fell from 86°C to 78°C.
Related Content
-
Where and How to Vent Injection Molds: Part 3
Questioning several “rules of thumb” about venting injection molds.
-
Why Shoulder Bolts Are Too Important to Ignore (Part 2)
Follow these tips and tricks for a better design.
-
How to Design Three-Plate Molds: Part 5
There are many things to consider, and paying attention to the details can help avoid machine downtime and higher maintenance costs. In this installment, the focus is on design and placement of sucker/puller pins.