Advantages of Servo-Driven Hydraulics For Large Injection Machines
Tips and Techniques: Servo-Driven Hydraulics
As injection molders continue to work to find ways to optimize their processes, energy efficiency continues to be a primary area of concern.
As injection molders continue to work to find ways to optimize their processes, energy efficiency continues to be a primary area of concern. For small and medium-sized parts, many molders have switched to all-electric molding machines, for which significant improvements in efficiency and overall energy savings are well documented.
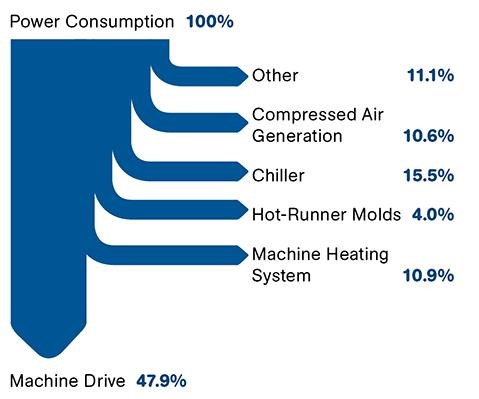
However, molders who are using high-tonnage hydraulic machines for molding large parts have faced serious issues trying to find cost-effective ways to achieve similar energy savings. Depending on the drive concept, hydraulic drives take up on average about 48% of the machine’s total energy consumption (see Fig. 1).
One recent advance in this area that shows great promise is the use of speed-controlled servo drives in place of the traditional fixed-speed, three-phase motors to drive the hydraulic pumps.
Traditional fixed-speed motors pump oil continuously, regardless of the needs of the various machine axes. Any excess volume of oil pumped is bled out over relief valves, which generates frictional heat in the oil, both shortening its life and requiring additional energy from the oil-cooling system. This wasteful pumping of unneeded oil volume is greatest during long clamp hold or cooling times.
Servo drives, however, can vary the pump speed—all the way to a dead stop, if appropriate—according to the system’s demand for oil. The longer cycles encountered in molding larger parts on large injection machines can benefit particularly from throttling back or stopping the hydraulic pump while the clamp is closed and the screw is not turning. Unlike a fixed-speed
pump, the servo drive can bring the pump to a dead stop during any breaks in molding.
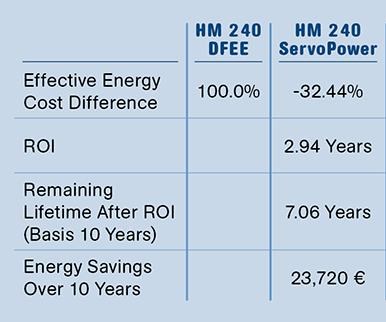
Use of servo-driven hydraulic pumps has shown significant energy savings—up to 35%—compared with conventional drives. Additionally, servo drives contribute to longer service life for the machine’s hydraulic oil, since it is heated less, and lower overall sound levels for the machine due to lower average motor speed.
EXPERIMENTAL VERIFICATION
In a recent experiment, Wittmann Battenfeld performed an economic comparison to study the difference in energy costs from the following three machines:
•A 240-ton Wittmann Battenfeld HM hydraulic machine with traditional fixed-speed hydraulic motor driving Bosch Rexroth DFEE variable-volume pumps.
•A 240-ton, Wittmann Battenfeld HM ServoPower hydraulic machine with servo-driven, variable-speed hydraulic pumps.
•A 240-ton, Wittmann Battenfeld EcoPower all-electric machine.
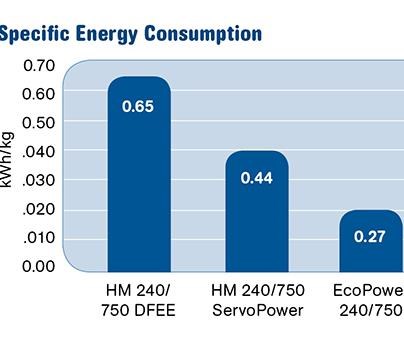
In this experiment, a machine benchmark study was calculated whereby each machine was operated running the same part, weighing 106 g, at the same cycle time, 20 sec. The results
are shown in Fig. 2.
While it is clear that the all-electric machine would deliver the best overall energy efficiency, it is also clear that in the case of the hydraulic machines, the model using the servo-driven hydraulic pumps would help the molder achieve far greater energy savings than the model using the traditional drives.
LONGER CYCLE TIMES
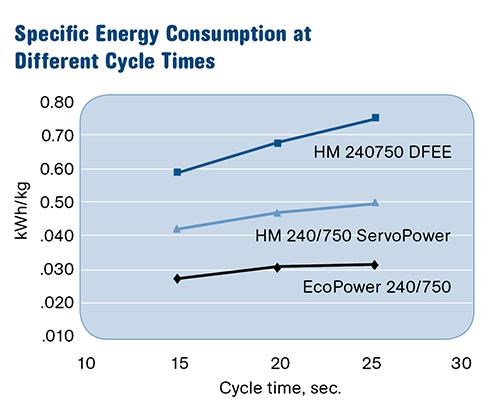
Large parts being produced on high-tonnage molding machines typically have long cycle times, and the benefits of the servo-driven hydraulic pumps in these instances are evident. For the same 240-ton machine comparison used to determine overall energy savings, it was determined that the longer the cycle time, the better the savings (Fig. 3).
As shown in Fig. 3, at a cycle time of 15 sec, the servo-driven hydraulic machine has an energy use of 0.39 kWh, while the machine with the traditional motor-driven pumps shows an
energy use of 0.58 kWh, nearly a 49% increase. When the energy usage is calculated for a 25-sec cycle, the servo-driven machine shows energy use of 0.47 kWh, while the traditional
drive machine shows energy use of 0.72 kWh, a 53% increase that would only get larger with even longer cycles.
Note that this experiment was conducted using 240-ton machines, primarily so the all-electric machine could be included. However, the differences in energy usage would be even larger with high-tonnage machines. Wittmann Battenfeld has employed the new servo-driven pumps as an option on its MacroPower line of large machines (400 to 1600 tons).
HOW IT WORKS
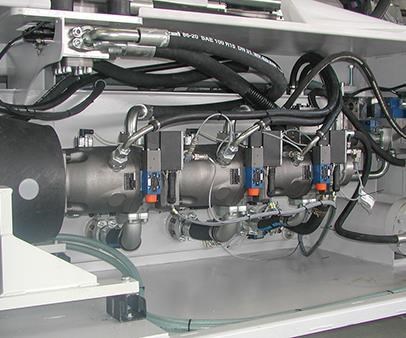
The conventional hydraulic pumps consist of a fixed-speed, three-phase motor with electrically adjustable, variable-volume pumps (Bosch Rexroth DFEE types), applying a modular, three-stage concept with parallel functions (Fig. 4). This concept makes possible a significant reduction in cycle times.
A speed-controlled servo drive (water-cooled) is available as an option (Fig. 5), which enables a reduction in energy consumption as well as the sound level. This concept is based on a highly dynamic servo motor instead of a three-phase motor with fixed speed.
The hydraulic pumps are again electrically adjustable axial piston pumps with a variable displacement volume. In this system, the oil delivery is regulated via the motor speed and the pivoting angle of the hydraulic pump.
In this way, the optimal relationship between the pump’s degree of efficiency and the motor speed is calculated for every operating point and regulated automatically by the machine’s control system.
Wittmann Battenfeld offers three different servo-driven pump systems, depending upon the user’s application:
•S1 ServoDrive package: Speed-controlled servo motor for the hydraulic pump.
•S2 ServoDrive package: Same as S1 plus an additional pump with servo motor for core-pull movement or parallel ejection.
•S3 ServoDrive package: Same as S2 plus hydraulic accumulator for fast injection.
Related Content
Compact Hybrid Injection Molding Machine Launched
Sumitomo Heavy Industries Ltd. (SHI) has introduced the iM18E, promising the smallest footprint in 20-ton machines.
Read MoreIPEX Opens Injection Molding Facility in North Carolina
The pipe and fittings manufacturer’s new 200,000-square-foot facility represents a $200 million investment and will create 150 jobs.
Read MoreFakuma 2023: Wittmann Battenfeld Expands All-Electric Line, Direct-Current Capabilities
Wittmann Battenfeld will introduce the new EcoPower B8X injection molding machine line and show direct current as an energy source for a concept machine that will power its own robot.
Read MoreTederic Promotes High Technology, Broader Market Presence
Four cells are running in its booth including a 1,300-ton multimaterial system highlighting its 2K capabilities.
Read MoreRead Next
See Recyclers Close the Loop on Trade Show Production Scrap at NPE2024
A collaboration between show organizer PLASTICS, recycler CPR and size reduction experts WEIMA and Conair recovered and recycled all production scrap at NPE2024.
Read MoreBeyond Prototypes: 8 Ways the Plastics Industry Is Using 3D Printing
Plastics processors are finding applications for 3D printing around the plant and across the supply chain. Here are 8 examples to look for at NPE2024.
Read MoreLead the Conversation, Change the Conversation
Coverage of single-use plastics can be both misleading and demoralizing. Here are 10 tips for changing the perception of the plastics industry at your company and in your community.
Read More