Novel PC/Polyester Blends Combine Stiffness and Ductility
An unusual balance of high modulus and ductile impact behavior is claimed for Xenoy HMD resins, recently launched by SABIC Innovative Plastics.
An unusual balance of high modulus and ductile impact behavior is claimed for Xenoy HMD resins, recently launched by SABIC Innovative Plastics. As we reported initially in November, these PC/PBT and PC/PET alloys achieve this combination of properties through the addition of a third thermoplastic ingredient that forms a nano-fibrillated network throughout the alloy matrix,
plus a patent-pending mineral filler of normal micron size. Six grades make up the initial Xenoy HMD slate. All are PC/PBT except for one high-heat PC/PET grade (X4870HH). One grade, IQ4840, incorporates PBT produced by chemical recycling of post-consumer PET.
Also in development is a flame-retardant version that achieves UL 94V-0 at 1.5 mm thickness and potentially down to 0.8 mm, as well as a high-flow version for thin-wall parts.
HOW THEY’RE DIFFERENT
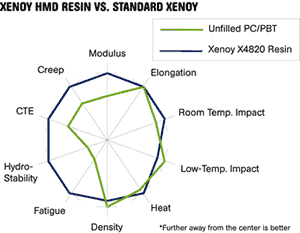
In previous PC/polyester blends, mineral fillers have been used to enhance stiffness or reduce coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), but at the expense of compromising ductility on impact, especially at low temperatures. In contrast, the ductility of an unfilled alloy is largely retained with the new HMD technology.
Further advantages over standard Xenoy grades are said to include excellent fatigue resistance, better creep resistance, good chemical resistance, low CTE (down to 4.5 vs. the usual 8), and around 8° C/15° F higher HDT than unfilled Xenoy. Good surface appearance, improved hydrolytic stability, and good weatherability and color retention are also claimed.
HMD blends typically process in the same way as regular PC/polyester blends, but with the advantage that the same grade can be used for injection molding, extrusion/thermoforming, and in some cases even blow molding. Potential applications include power-tool housings, sports and safety equipment, and automotive energy absorbers, door handles, and fuel-tank flaps. While the company would not comment on pricing of the new grades, SABIC sources did say the enhanced performance of HMD grades allows for thinner walls, reducing the overall part cost.
In the accompanying table, the current HMD grades are compared with two standard Xenoy resins: CL100B, a general-purpose unfilled grade for unpainted automotive exterior parts, and X5410, a mineral-filled PC/PET for painted auto exterior parts.
| NEW XENOY HMD COMPOUNDS VS. STANDARD GRADES | ||||||||
CL100B Std. Unfilled | X4810 HMD | X4820 HMD | X4830 HMD | iQ4840 HMD | X4850 HMD | X4870HH HMD | X5410 Std. Min. Filled | |
| MECHANICAL | ||||||||
| Tensile Mod., GPa | 2.2 | 2.75 | 3.0 | 3.2 | 3.8 | 3.85 | 4.3 | 3.2 |
| Tensile Str. @ Yield, MPa | 55 | 55 | 52 | 60 | 62 | 58 | 63 | 55 |
| Elong. @ Break, % | 75 | 100 | 100 | 120 | 100 | 80 | 10 | 12 |
| Flex. Mod., GPa | 2.2 | 2.5 | 2.85 | 2.9 | 3.45 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 2.7 |
| Flex. Str. @ Yield, MPa | 85 | 87 | 87 | 90 | 96 | 94 | 98 | 93 |
| IMPACT | ||||||||
| Notched Izod, kJ/m2 23 C | 46 | 50 | 55 | 45 | 20 | 20 | 10 | 7 |
| 0° C | -- | 20 | 30 | 15 | -- | 11 | -- | -- |
| -30 C | 21 | 12 | 15 | 9 | -- | 7 | 6 | 7 |
| THERMAL | ||||||||
| Vicat Temp., C | 129 | 133 | 134 | 135 | 128 | 135 | 139 | 140 |
| HDT, C 0.45 MPa | 110 | 115 | -- | 119 | 116 | 121 | 131 | 128 |
| 1.8 MPa | 90 | 91 | 94 | 97 | 98 | 99 | 113 | 105 |
| CTE, 1/10-5 °C | 9 | 8 | -- | 7.2 | -- | 6.3 | 4.8 | 5.8 |
| PHYSICAL | ||||||||
| Density, g/cc | 1.22 | 1.25 | 1.26 | 1.27 | 1.3 | 1.31 | 1.34 | 1.26 |
| Mold Shrinkage, Flow Dir., % | 0.7-1.0 | 0.7-0.9 | 0.5-0.9 | 0.7-0.9 | 0.7-0.9 | 0.7-0.9 | 0.5-0.7 | 0.7-0.8 |
Related Content
-
Prices for All Volume Resins Head Down at End of 2023
Flat-to-downward trajectory for at least this month.
-
Scaling Up Sustainable Solutions for Fiber Reinforced Composite Materials
Oak Ridge National Laboratory's Sustainable Manufacturing Technologies Group helps industrial partners tackle the sustainability challenges presented by fiber-reinforced composite materials.
-
Tracing the History of Polymeric Materials, Part 26: High-Performance Thermoplastics
The majority of the polymers that today we rely on for outstanding performance — such as polysulfone, polyethersulfone, polyphenylsulfone and PPS — were introduced in the period between 1965 and 1985. Here’s how they entered your toolbox of engineering of materials.