Materials Know How
A Processor’s Most Important Job, Part 4: Mold Temperature
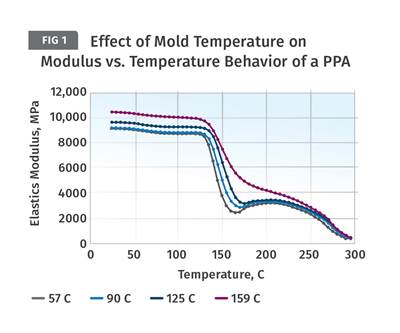
Engineering polymers require higher mold temperatures to achieve their ideal structure. The temptation to turn down the mold temperatures can hurt part performance.
Read MoreA Processor’s Most Important Job, Part 3: Unintended Consequences
Processors are often expected to compensate for ill-advised decisions made earlier in the product-development process. In the case of shrinkage, one of the most common ‘fixes’ is to simply reduce the mold temperature.
Read MoreA Processor’s Most Important Job, Part 2: Crystallinity
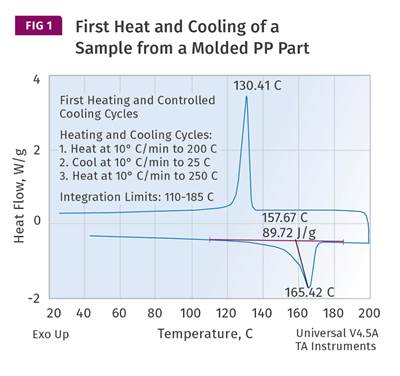
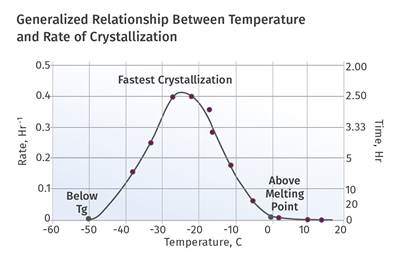
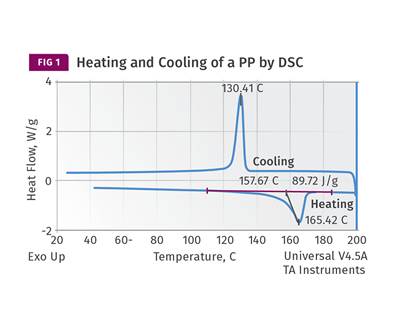
Process conditions help determine the difference between the maximum degree of crystallinity that can be achieved in a polymer and the degree that is present in a molded part.
Read MoreA Processor’s Most Important Job, Part 1: Molecular Weight
Many processors don’t realize that preserving material characteristics is crucial to product success and failure. The focus here is on molecular weight.
Read MoreMaterials: Cycle Time—Science vs. Rules of Thumb, Part 6
This installment—on elastomers—completes a series, whose theme is to bring more science to the discipline of molding. The overall message: Ask a lot of questions whenever someone posits this or that ‘rule of thumb’ about processing.
Read MoreMaterials: Cycle Time: Science vs. Rules of Thumb—Part 5
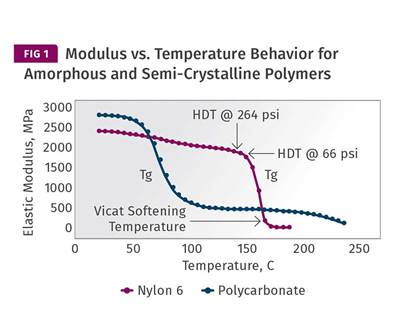
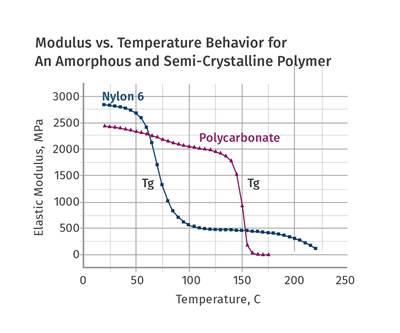
Let’s examine the behavior of semi-crystalline materials that never reach their glass-transition temperature as they cool.
Read MoreCycle Time: Science vs. Rules of Thumb—Part 4
While laboratory tests are helpful in determining how polymers behave, you must remember the fundamental differences between laboratory measurements and the real world of plastic processing. Let’s examine semi-crystalline polymers here.
Read MoreMaterials—Cycle Time: Science vs. Rules of Thumb—Part 3
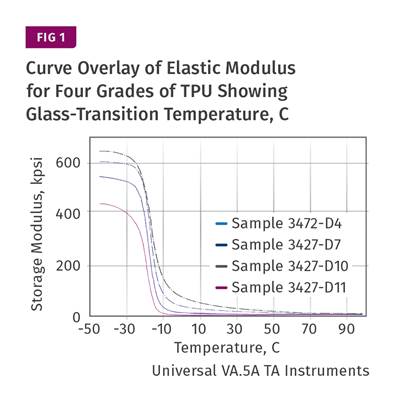
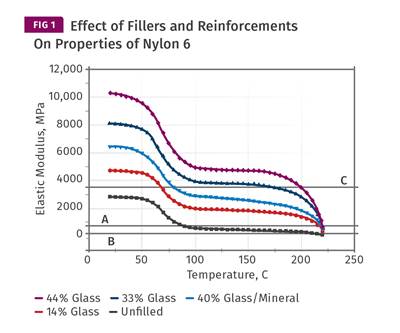
To properly calculate cycle time, you need to understand how the modulus of a polymer increases as it cools in the mold.
Read MoreMaterials: Cycle Time: Science vs. Rules of Thumb—Part 2
Understanding cooling—how a given material develops modulus as it solidifies—requires access to data that provides some insight into the relationship between modulus and temperature. Dynamic mechanical analysis is a helpful tool.
Read MoreCycle Time: Science vs. Rules of Thumb, Part 1
What temperature must the polymer reach so the part can be ejected from the mold? Here, more than for any other variable, ‘rules of thumb’ unfortunately prevail.
Read More