Extrusion Know How
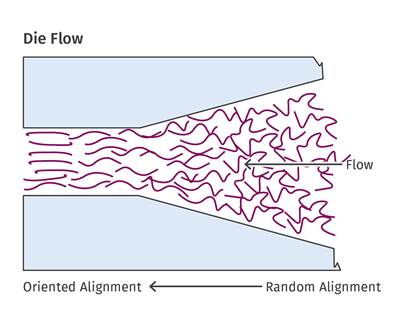
EXTRUSION: Orientation: The Good and the Bad
Depending on what you are trying to accomplish, molecular orientation can have a positive or negative impact on your part. Here’s how to control it.
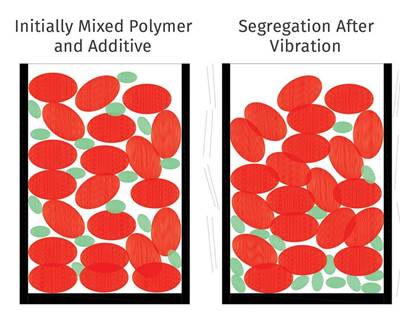
Read MoreEXTRUSION: Better Mix In Means Better Mix Out
Segregation or de-mixing of polymers and additives can be a big problem in single-screw extrusion. Here’s why it happens, and how to fix it.
Read MoreEXTRUSION: How Slow Can You Go?
Larger screws designed for high outputs will generate a variety of problems if run too slowly. Here’s why.
Read MoreEXTRUSION: Finding the Sweet Spot in Screw Design
The compression ratio of a screw does not provide enough detail on how it will perform. Screw design is a balancing act that takes many variables into account.
Read MoreEXTRUSION: Understanding The Barrier Gap
All barrier screws are not created equal, and the barrier length and gap can be one of the reasons.
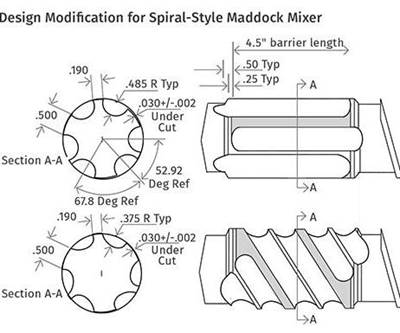
Read MoreEXTRUSION: Venerable Maddock Mixer Still an Extrusion Workhorse
Variations to this decades-old mixing section are widely used, but processors should carefully analyze these designs and not assume they will perform better.
Read MoreEXTRUSION: Managing Regrind
Reusing scrap is a necessary evil. But be aware of the negative impact scrap has on properties and extrusion efficiencies. Start by developing a regrind-usage program.
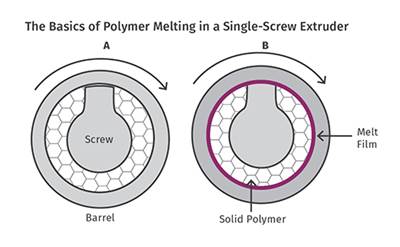
Read MoreEXTRUSION: Melting 101
Learn the basics on how polymer melts in a single screw. Barrel temperature plays less of a role than you might think.
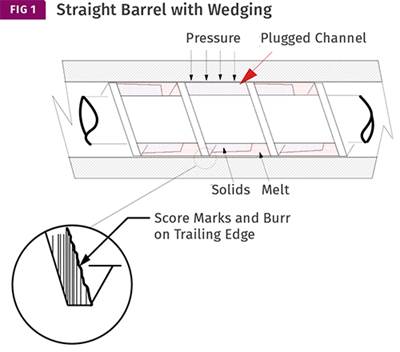
Read MoreEXTRUSION: The Two Main Causes of Screw Wear
Wedging and misalignment are often confused with each other when inspecting a worn screw.
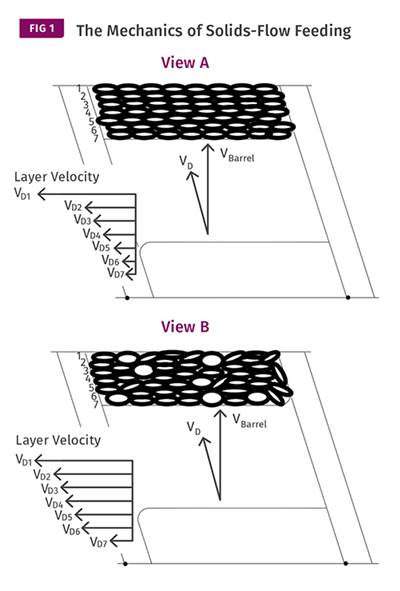
Read MoreEXTRUSION: Pellet Geometry Can Impact Output
A simple angle-of-repose experiment can help you determine how your pellets will feed.
Read More